
Supercondensateur / Supercapacitor
500 F 2,7V

Pour les condensateurs en série vous pouvez utiliser un module de protection pour supercondensateur.
Les module de protection permet de charger les condensateurs en série en limitant le courant à 1A et la tension à 2,6V
pour chaque condensateur.
*****
For
capacitors in series, you can use a supercapacitor protection module.
This protection module allows you to charge capacitors in series while limiting
the current to 1A and the voltage to 2,6V for each capacitor.
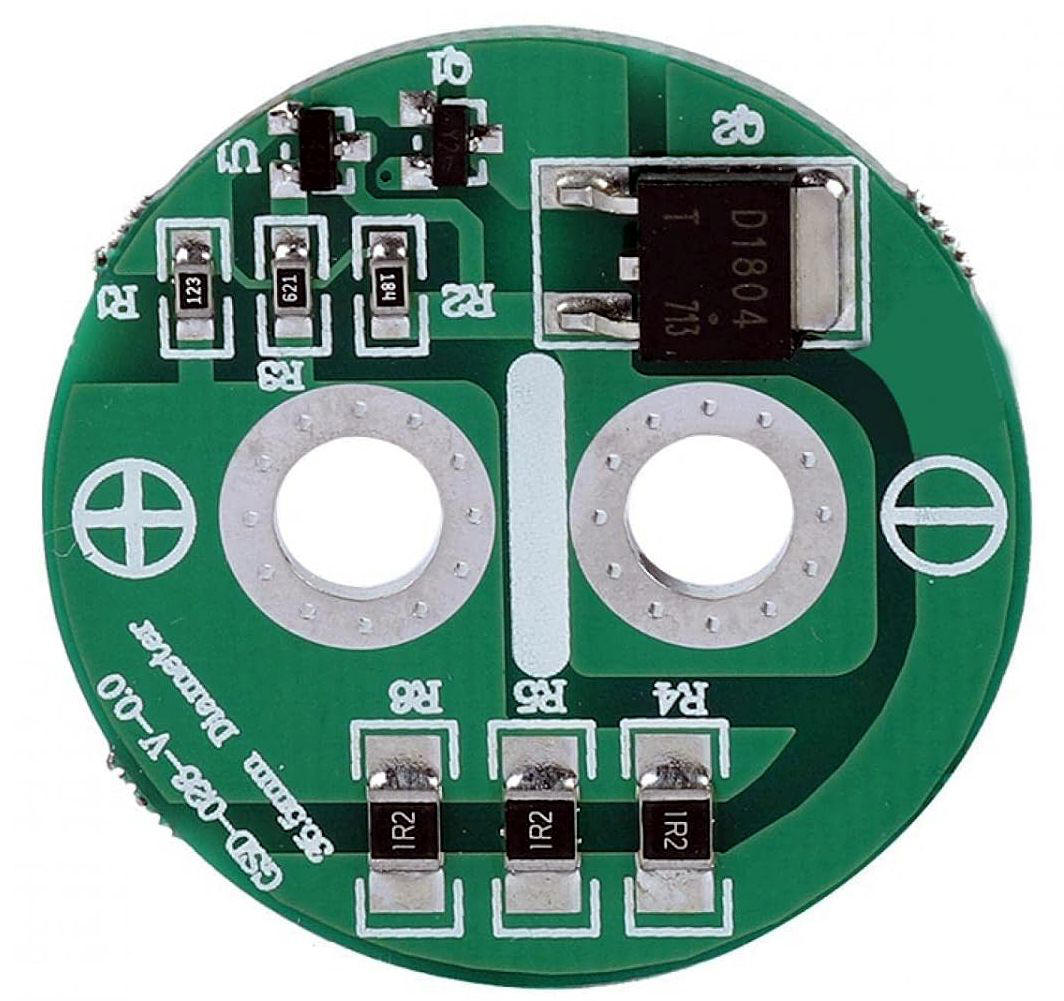


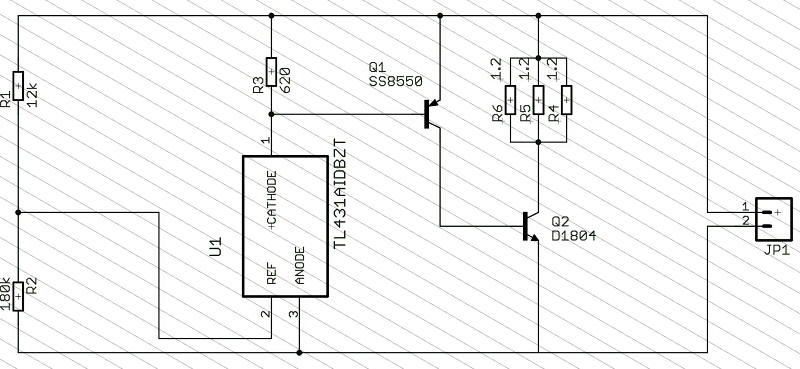
Il s'agit d'un circuit simple composé d'une référence de précision programmable TL431 (U1), d'un transistor PNP à usage général SS8550 (Q1) et d'un transistor de puissance NPN D1804 (Q2).
Les trois résistances de découplage (R4-R5-R6) de 1,2 Ω supportent un courant
maximal de 1A.
Notez que lorsque la
tension du supercondensateur atteint la valeur de consigne de 2,66 V, le
transistor de puissance NPN Q2 est activé (la formule pour le TL431 est V = (1 +
R1/R2) × 2,5). Ce circuit protège ainsi les supercondensateurs de 2,7 V
lorsqu'ils sont chargés en série.
Comme souvent, de nombreuses variantes de cette carte chinoise sont désormais disponibles dans les boutiques en ligne.
*****
This is a simple circuit consisting of a programmable precision reference TL431 (U1), general purpose PNP transistor SS8550 (Q1) and NPN power transistor D1804 (Q2).
The 1.2Ωx3 “bypass” chip resistors (R4-R5-R6) can handle up to 1A of current.
Note that when the supercapacitor voltage reaches the setting point 2.66V, the NPN power transistor Q2 is turned on (The formula for the TL431 is V= (1+R1/R2)x2.5).
Thus this circuit protects the 2.7V supercapacitors when they are charged in series. As usual, many variants of this Chinese board are now available through online stores.
Installation Permanente / Permanent Installation


Installation amovible / Removable installation
| Vous pouvez
expérimenter avec n'importe lequel supercondensateur. (ex. 10F, 70F, 500F) |
You can
experiment with any supercapacitor. (e.g., 10F, 70F, 500F) |
|
Des Boulon M3, une plus longue pour le positif et des rondelles. |
M3 bolts, a longer one for the positive terminal, and washers. |
| Du fils flexible en silicone AWG 20. | AWG 20 flexible silicone wire. |
| Des pinces alligators et des connecteurs ronds. | Alligator clips and round connectors. |
| Souder les fils aux pinces et aux connecteurs. | Solder the wires to the clamps and connectors. |
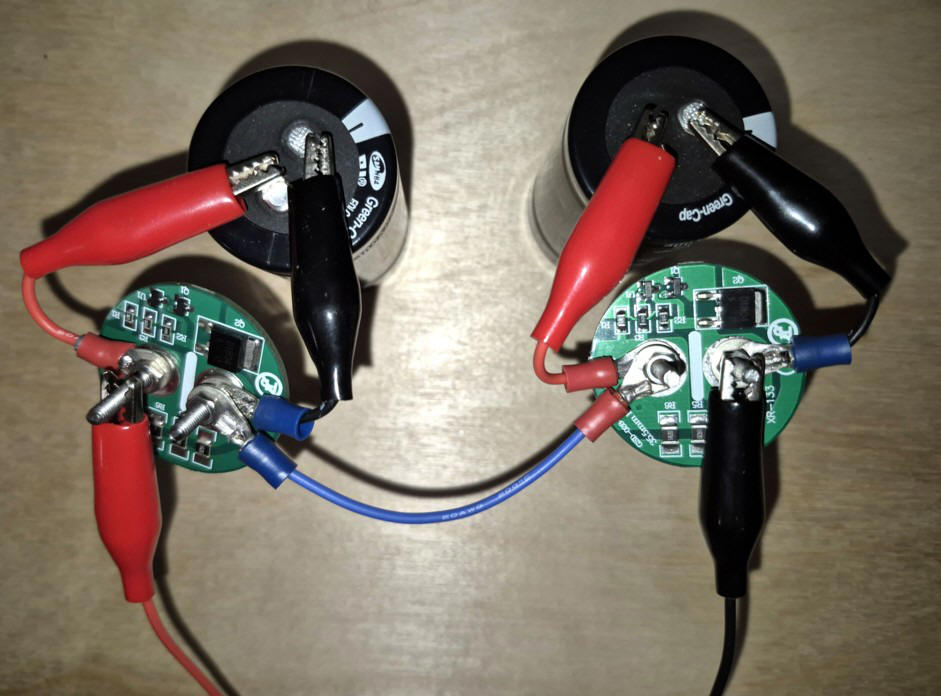
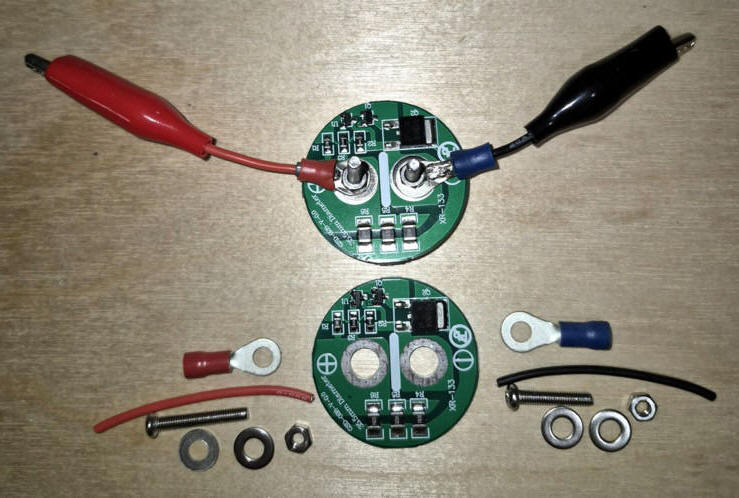


|
On peut utiliser les supercondensateurs comme alimentation de
secours. On les connecte en série pour avoir la tension désirée. |
Supercapacitors can be used as a backup power supply. They are connected in series to obtain the desired voltage. |
|
Les condensateurs à double couche électrique (EDLC), ou
supercondensateurs, offrent une technologie complémentaire aux
batteries. Tandis que les batteries peuvent fournir de l'énergie pendant des périodes relativement longues, les supercondensateurs peuvent fournir de l'énergie rapidement pendant de courtes périodes. Les supercondensateurs sont également respectueux de l'environnement, ne sont pas sujets à l'emballement thermique et peuvent fonctionner de manière fiable pendant 20 ans. Ils peuvent être utilisés comme seule méthode de stockage d'énergie, en combinaison avec des batteries, ou comme dispositif hybride pour optimiser la fourniture d'énergie. Longue durée de vie : Les supercondensateurs ont une durée de vie allant jusqu'à 10 à 15 ans, soit plus longue que celle de nombreuses batteries. Nombre de cycles élevé : Ils peuvent supporter de 8 à 120 millions de cycles de charge/décharge, selon le modèle, ce qui est beaucoup plus élevé que celui des batteries traditionnelles. |
Electric double-layer capacitors (EDLCs), or supercapacitors, offer
a complementary technology to batteries. While batteries can provide energy for relatively long periods, supercapacitors can provide energy quickly for short periods. Supercapacitors are also environmentally friendly, not prone to thermal runaway, and can operate reliably for 20 years. They can be used as a standalone energy storage method, in combination with batteries, or as a hybrid device to optimize energy supply. Long lifespan: Supercapacitors have a lifespan of up to 10 to 15 years, which is longer than that of many batteries. High number of cycles: They can withstand 8 to 120 million charge/discharge cycles, depending on the model, which is much higher than that of traditional batteries. |
 |
|
|
La capacitance total Ct = C divisé par le nombre de condensateurs. La tension total Vt = Somme de tous les tentions des condensateurs. Ct = C / Nc Vt = Vc1 + Vc2 .... + Vcn |
The total capacitance Ct = C divided by the number of capacitors. The total voltage Vt = Sum of all the capacitor voltages. Ct = C / Nc Vt = Vc1 + Vc2 ... + Vcn |
|
Pour charger le condensateur 500 F Avec le power supply Limiter le courant à 1A. Sans un module de protection La tension doit être Max 2,7V. Charger jusqu'à l'ampérage soit très bas. Prend environs de 22 à 70 par minutes condensateur. |
To charge the 500F capacitor Using the power supply Limit the current to 1A. Without a protection module The voltage must be a maximum of 2.7V. Charge until the amperage is very low. Takes approximately from 22 to 70 minutes per capacitor. |
| Le tableau ci-dessous indique le nombre de condensateurs requis et la tension de charge pour chaque circuit soit de 1,5V à 12V. | The table below indicates the number of capacitors required and the charging voltage for each circuit, from 1.5V to 12V. |
Exemple
Pour un circuit 5V / for a 5V circuit
Connecter en série
2 condensateurs de 500 F 2,7 V / Connect two 500 µF 2.7V capacitors in series
500 F / 2 = 250 F
5 V / 2 = 2,5 V
Charger les condensateurs / Charging the capacitors
Avec un module de protection / With a protection module
1.
Pour avoir une tension également répartie entre chaque condensateur et éviter des dommages possibles, assurez vous que les condensateurs sont déchargés avant de les connecter au modules.
Pour décharger un condensateur, j'ai utilisé 6 globes halogène de 12V 10W connectés en parallèle, ce qui donne une résistance de 0,2Ω de 60W.
To ensure even voltage distribution between each capacitor and to avoid possible damage, make sure the capacitors are discharged before connecting them to the modules.
To discharge a capacitor, I used 6 12V 10W halogen globes connected in parallel, which gives a resistance of 0.2Ω of 60W.
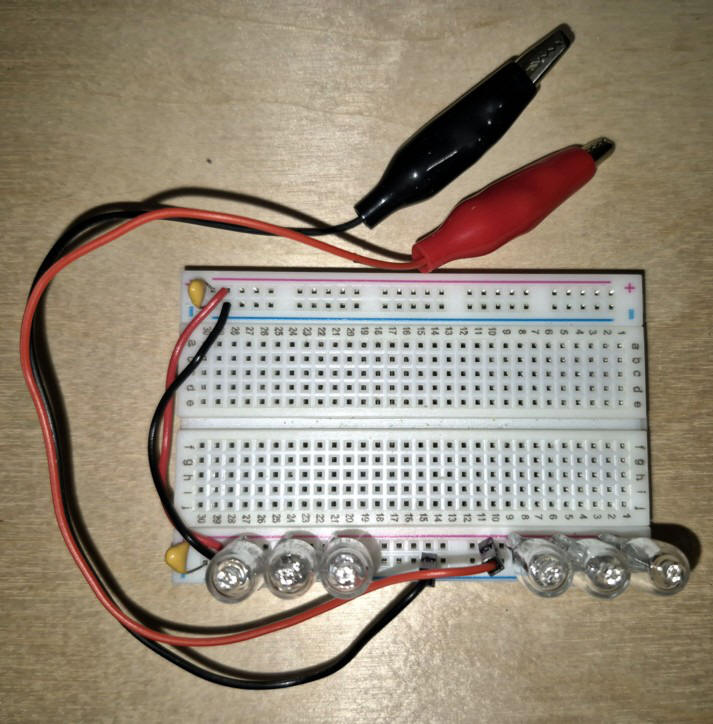
2.
Connecter en série le nombre de condensateurs nécessaire pour la tension du circuit désirée.
Voir le tableau de charge ci-dessous.
Connect the
required number of capacitors in series to achieve the desired circuit voltage.
See the load table below.
3.
Charger les condensateurs connecter en série selon la tension du circuit requise.
Limiter le courant à 1A.
Charge the capacitors connected in series according to the required circuit voltage.
Limit the current to 1A.
Sans un module de protection / Without a protection module
1.
Charger les condensateurs individuellement
Charge the capacitors individually
2.
Connecter en série les condensateurs chargés dans votre circuit
Connect the charged capacitors in series in your circuit
Tableau de charge / Load table 500 F 2,7V - 1A
|
Tension du circuit Circuit voltage |
Nombre de condensateurs Number of capacitors Nc en séries / in series |
Tension de charge du condensateur Charging voltage of the capacitor |
Farad Total Total Farad Ct = C / Nc |
| V | S | V | F |
| 1,5 V | 1 | 1,5 V | 500 F |
| 3 V | 2 S | 1,5 V | 250 F |
| 5 V | 2 S | 2,5 V | 250 F |
| 9 V | 4 S | 2,25 V | 125 F |
| 12 V | 5 S | 2,4 V | 100 F |
Limiter le courant à 1A / Limit the current to 1A.
|
Si vous possédez une alimentation de laboratoire bon marché
compatible avec la protection contre les surintensités (mode CC) et
que la seule façon de régler ou de vérifier la limite de courant
maximale consiste à court-circuiter les sorties de l'alimentation,
puis effectuer le réglage. 1. Régler la tension à 1V - 2V. |
If you have an inexpensive lab power supply with overcurrent
protection (DC mode) and the only way to set or check the maximum
current limit is to short-circuit the power supply outputs and then
make the adjustment: 1. Set the voltage to 1V–2V. |
 |
|
|
2. Court-circuiter les sorties de l'alimentation 3. puis effectuer le réglage |
2. Short-circuit the power supply outputs 3. and then make the adjustment. |
 ---->
---->
 |
|
| Avant de
charger, j'ai mesurer la tension de deux de mes supercondensateurs neuf: 106.6 mV et 133.7 mV |
Before
charging, I measured the voltage of two of my new supercapacitors: 106.6 mV and 133.7 mV |
| J'ai commencé
par charger deux condensateur à 1,5V pour ensuite les brancher en série
pour obtenir une tension de 3V. J'ai arrêter de charger les condensateurs à 0,094 A J'ai obtenue une tension de 1,448V pour un condensateur et 1.502 V pour l'autre. |
I started by
charging two capacitors to 1.5V and then connected them in series to
obtain a voltage of 3V. I stopped charging the capacitors at 0.094 A. I obtained a voltage of 1.448 V for one capacitor and 1.502 V for the other. |
Début de la charge / Start of charging |
Fin
de la charge / End of charge |
| Ensuite je les
ai charger à 2.5v pour obtenir une tension de 5V. |
Then I charged them to 2.5v to obtain a voltage of 5V. |
 |
 |
|
Avec les deux condensateurs à 5V, j'ai fais fonctionner ce circuit qui
fonctionne sous une tension de 3V à 5V, pendant: 8h avec une tension de 2.3 V 9h avec une tension de 2.138 V |
With the two 5V capacitors, I ran this circuit, which operates under a
voltage of 3V to 5V, for: 8 hours with a voltage of 2.3 V 9 hours with a voltage of 2.138 V |
 |
|
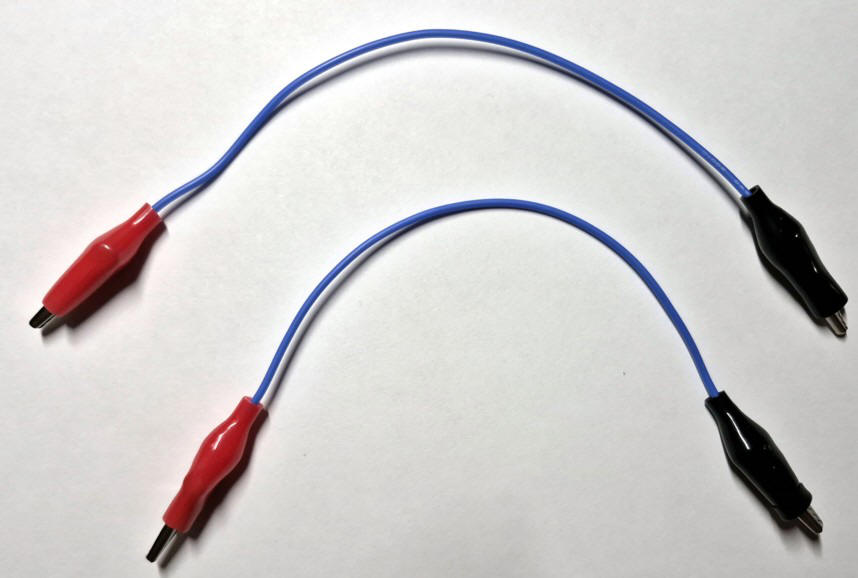
| Vous pouvez vous faire des fils pour les connexions en série. | You can make your own wires for series connections. |
 |
|
|
On peut charger tous les supercondensateurs de la même façon. Mais pour des supercondensateurs inférieur à 100 F limiter le courant à 500 mA.
|
All supercapacitors can be charged in the same way. However, for supercapacitors smaller than 100 F, limit the current to 500 mA. |
Tableau de charge / Load table 70 F 2,7V - 500 mA
|
Tension du circuit Circuit voltage |
Nombre de condensateurs Number of capacitors |
Tension de charge du condensateur Charging voltage of the capacitor |
Farad Total Total Farad |
| 1,5 V | 1 | 1,5 V | 70 F |
| 3 V | 2 | 1,5 V | 35 F |
| 5 V | 2 | 2,5 V | 35 F |
| 9 V | 4 | 2,25 V | 17,5 F |
Tableau de charge / Load table 15 F 2,7V - 500 mA
|
Tension du circuit Circuit voltage |
Nombre de condensateurs Number of capacitors |
Tension de charge du condensateur Charging voltage of the capacitor |
Farad Total Total Farad |
| 1,5 V | 1 | 1,5 V | 15 F |
| 3 V | 2 | 1,5 V | 7,5 F |
| 5 V | 2 | 2,5 V | 7,5 F |
| 9 V | 4 | 2,25 V | 3,75 F |
Tableau de charge / Load table 10 F 2,7V - 500 mA
Tableau de charge / Load table 10 F 2,7V - 500 mA
|
Tension du circuit Circuit voltage |
Nombre de condensateurs Number of capacitors Nc en séries / in series |
Tension de charge du condensateur Charging voltage of the capacitor |
Farad Total Total Farad Ct = C / Nc |
| V | S | V | F |
| 1,5 V | 1 | 1,5 V | 10 F |
| 3 V | 2 S | 1,5 V | 5 F |
| 5 V | 2 S | 2,5 V | 5 F |
| 9 V | 4 S | 2,25 V | 2,5 F |
Tableau de charge / Load table 15 F 2,7V - 500 mA
|
Tension du circuit Circuit voltage |
Nombre de condensateurs Number of capacitors Nc en séries / in series |
Tension de charge du condensateur Charging voltage of the capacitor |
Farad Total Total Farad Ct = C / Nc |
| V | S | V | F |
| 1,5 V | 1 | 1,5 V | 15 F |
| 3 V | 2 S | 1,5 V | 7,5 F |
| 5 V | 2 S | 2,5 V | 7,5 F |
| 9 V | 4 S | 2,25 V | 3,75 F |
Tableau de charge / Load table 70 F 2,7V - 500 mA
|
Tension du circuit Circuit voltage |
Nombre de condensateurs Number of capacitors Nc en séries / in series |
Tension de charge du condensateur Charging voltage of the capacitor |
Farad Total Total Farad Ct = C / Nc |
| V | S | V | F |
| 1,5 V | 1 | 1,5 V | 70 F |
| 3 V | 2 S | 1,5 V | 35 F |
| 5 V | 2 S | 2,5 V | 35 F |
| 9 V | 4 S | 2,25 V | 17,5 F |
Charger les condensateurs / Charging the capacitors
Avec un module de protection / With a protection module
Limiter le courant à 1A.
Pour avoir une tension également répartie entre chaque condensateur et éviter des dommages possibles, assurez vous que les condensateurs sont déchargés avant de les connecter au modules.
Pour décharger un condensateur, j'ai utilisé 6 globes halogène de 12V 10W connectés en parallèle, ce qui donne une résistance de 0,2Ω de 60W.
Limit the current to 1A.
To ensure even voltage distribution between each capacitor and to avoid possible damage, make sure the capacitors are discharged before connecting them to the modules.
To discharge a capacitor, I used 6 12V 10W halogen globes connected in parallel, which gives a resistance of 0.2Ω of 60W.
| Avant / Before | Après / After | ||||||||
| Test No. | Vt | Vc1 | Vc2 | Vc3 | Vc4 | Vc1 | Vc2 | Vc3 | Vc4 |
| 1 | 3V, 2S | 0.429V | 0.428V | -- | -- | 1.495 | 1.407 | -- | -- |
| 2 | 5V, 2S | 1.519V | 0.379V | -- | -- | 2.61V | 2.33V | -- | -- |
| 3 | 9V, 4S | 0.185V | 0.202V | 0.143V | 0.296V | 2.58V | 2.28V | 1.73V | 2.22V |
| 4 | 5V, 2P + 2S | 0.692V | 0.692V | 0.644V | 0.644V | 2.46V | 2.44V | 2.38V | 2.39V |
| (c1+c2) + (c3+c4) | P | P | |||||||
Note: Supercondensateurs en séries S et en parallèles P / Supercapacitors in series S and parallel P , (P + S)
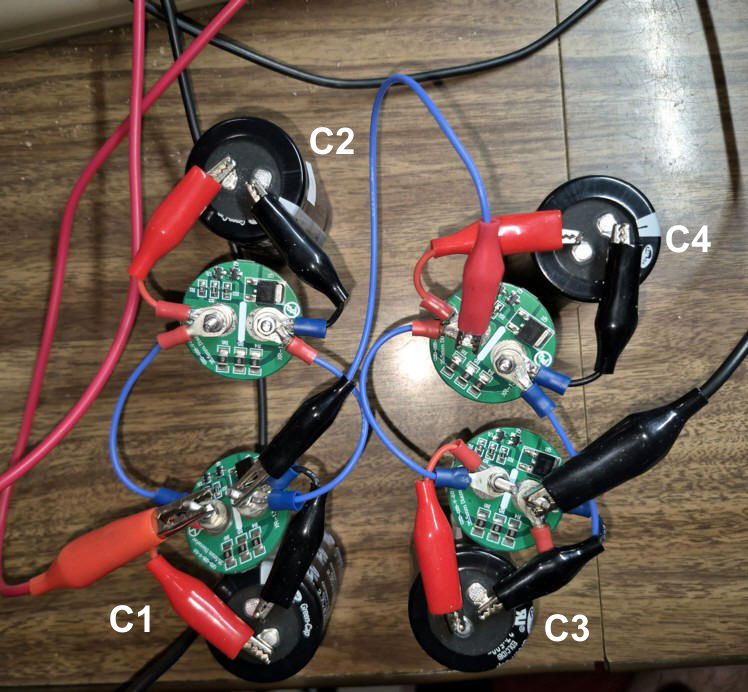
Supercondensateurs en parallèles / Supercapacitors parallel
En parallèle les Farads s'additionne et la tensions reste la même
In parallel, the Farads add up and the voltage remains the same.

Ct = Ct * Nc
Vt = Vcn
Pour un circuit de 1,5V / For a 1.5V circuit
|
Nombre de condensateurs Number of capacitors |
Supercondensateurs Supercapacitors Farad |
Farad Total Total Farad |
| 1 | 500 | 5000 F |
| 70 | 70 F | |
| 15 | 15 F | |
| 10 | 10 F | |
| 2 | 500 | 1000F |
| 70 | 140 F | |
| 15 | 30 F | |
| 10 | 20 F | |
| 3 | 500 | 1500 F |
| 70 | 210 F | |
| 15 | 45 F | |
| 10 | 40 F | |
| 4 | 500 | 2000 F |
| 70 | 280 F | |
| 15 | 60 F | |
| 10 | 40 F |
Supercondensateurs en séries S et en parallèles P / Supercapacitors in series S and parallel P , (P + S)
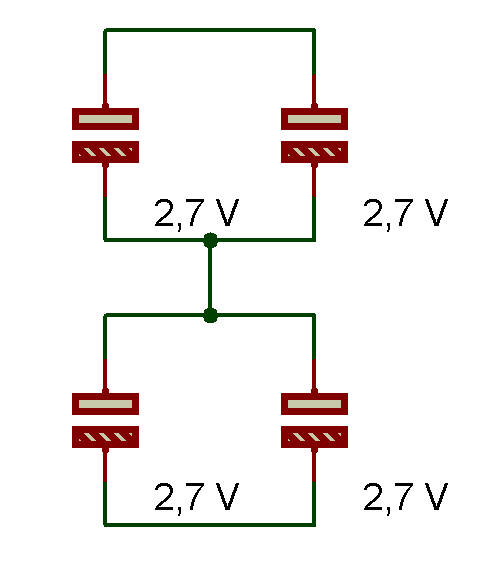 |
= 2P + 2S |
Tableau de charge / Load table
|
Tension du circuit Circuit voltage |
Nombre de condensateurs Number of capacitors en séries / in series |
Tension de charge du condensateur Charging voltage of the capacitor |
| V | S | V |
| 1,5 V | 1 | 1,5 V |
| 3 V | 2 S | 1,5 V |
| 5 V | 2 S | 2,5 V |
| 9 V | 4 S | 2,25 V |
P + S , Farad Total / Total Farad
|
Nombre de condensateurs Number of capacitors SP |
Supercondensateurs Supercapacitors Farad |
Farad Total Total Farad |
|
2 P + 2 S 4 SP Vt = Vc * 2 |
500 | 500 * 2 / 2 = 500 F |
| 70 | 70 * 2 / 2 = 70 F | |
| 15 | 15 * 2 / 2 = 15 F | |
| 10 | 10 * 2 / 2 = 10 F | |
|
2 P + 3 S 5 SP Vt = Vc * 3 |
500 | 500 * 2 / 3 = 333.3 F |
| 70 | 70 * 2 / 3 = 46.6 F | |
| 15 | 15 * 2 / 3 = 10 F | |
| 10 | 10 * 2 / 3 = 6.6 F | |
|
2 P + 4 S 6 SP Vt = Vc * 4 |
500 | 500 * 2 / 4 = 250 F |
| 70 | 70 * 2 / 4 = 35 F | |
| 15 | 15 * 2 / 4 = 7.5 F | |
| 10 | 10 * 2 / 4 = 5 F | |
|
3 P + 2 S 5 SP Vt = Vc * 3 |
500 | 500 * 3 / 2 = 750 F |
| 70 | 70 * 3 / 2 = 105 F | |
| 15 | 15 * 3 / 2 = 22.5 F | |
| 10 | 10 * 3 / 2 = 15 F | |
|
3 P + 3 S 6 SP Vt = Vc * 3 |
500 | 500 * 3 / 3 = 500 F |
| 70 | 70 * 3 / 3 = 70 F | |
| 15 | 15 * 3 / 3 = 15 F | |
| 10 | 10 * 3 / 3 = 10 F | |
|
3 P + 4 S 7 SP Vt = Vc * 4 |
500 | 500 * 3 / 4 = 375 F |
| 70 | 70 * 3 / 4 = 52.75 F | |
| 15 | 15 * 3 / 4 = 11.25 F | |
| 10 | 10 * 3 / 4 = 7.5 F | |
|
4 P + 2 S 6 SP Vt = Vc * 2 |
500 | 500 * 4 / 2 = 1000 F |
| 70 | 70 * 4 / 2 = 140 F | |
| 15 | 15 * 4 / 2 = 30 F | |
| 10 | 10 * 4 / 2 = 20 F | |
|
4 P + 3 S 7 SP Vt = Vc * 3 |
500 | 500 * 4 / 3 = 666.6 F |
| 70 | 70 * 4 / 3 = 93.3 F | |
| 15 | 15 * 4 / 3 = 19.9 F | |
| 10 | 10 * 4 / 3 = 13.3 F | |
|
4 P + 4 S 8 SP Vt = Vc * 4 |
500 | 500 * 4 / 4 = 500 F |
| 70 | 70 * 4 / 4 = 70 F | |
| 15 | 15 * 4 / 4 = 15 F | |
| 10 | 10 * 4 / 4 = 10 F |